There are several ways that investors and traders can help limit risk. One of these is hedging.
What is the essence of hedging, what is it and how does it work on a real example
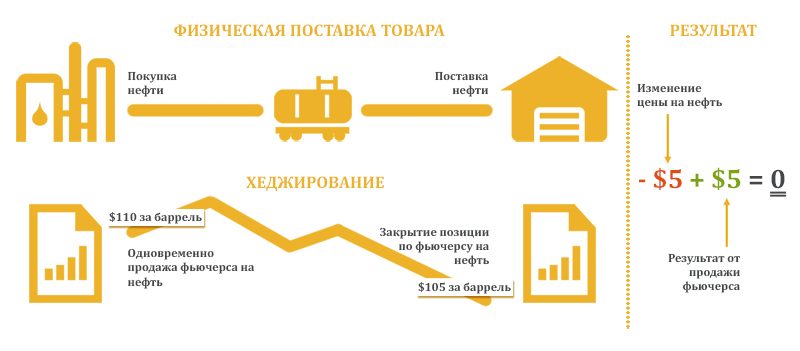
Hedging is a measure to reduce the risks that arise in financial markets. In essence, you make a reverse trade to compensate for possible losses on a previously opened position.
Example:
Let’s say you own a Gazprom share. Due to a possible correction in gas prices and geopolitics, you are afraid that the stock quotes will fall. In this case, you can resort to hedging. That is, open a position on the fall of the stock. If this does not happen, then you will lose a little. Only a small part of the capital, which was put on the fall. But if the papers of Gazprom collapse, then you will make a profit on a short deal. It will cover losses on a previously opened position.
- Hedge Funds . They professionally manage other people’s capital and apply various strategies related to limiting market risks.
- Exporters and Importers . Such companies insure the risks associated with the disruption of supply chains or changes in the exchange rate.
- Traders . Speculators open reverse positions on the same instrument. The goal is to reduce the risk of volatility in trading.
- Large investors . They insure portfolio risks by country, currency and industry.
Hedge is available not only to big players. It is also used by small private investors with little capital.
Why do you need risk hedging in simple words
The safety tool is used for the following purposes:
- Protection of a long position in case of a possible fall in the asset. You can open a Short trade on the same paper. If you change the price rate, you will lose almost nothing.
- Insurance for a short trade in case of an increase in the asset price. To do this, you need to open a Long position on the same instrument. This will insure against volatility.
- Hedge against changes in the exchange rate. Currency risk hedging is a way to protect your finances in case of fluctuations in the foreign exchange rate.
- Reducing operational risks specific to the business cycle. For example, a hedge is used in case of violation of delivery dates.
- Elimination of uncertainty. If you do not have a clear plan for what will happen to the market in the near future, then you can resort to a hedge. Buy inverse instruments and insure capital against possible changes in value.
Types of hedging on the exchange, in trading and not on the exchange
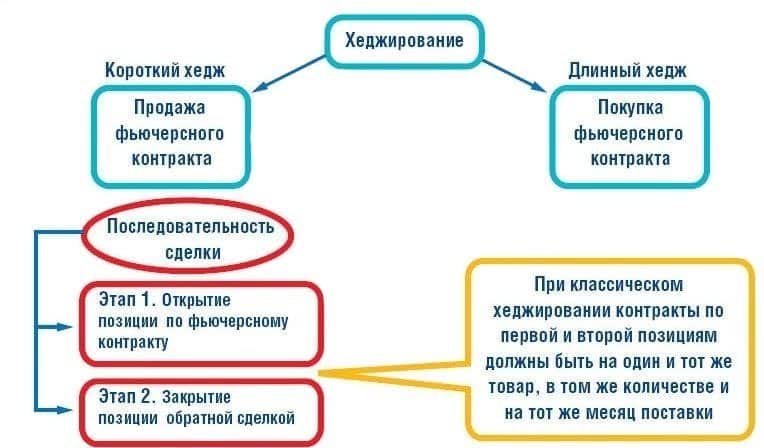
There are several classifications of hedge. All of them depend on the subject. Let’s consider the most basic ones. By type of instrument:
- Exchange – contracts that are drawn up on the exchange. Popular hedging instruments are options and futures. They help to insure financial risks. The third party in the transaction is the clearing house. She is responsible for the execution and delivery of the contract.
- OTC – contracts that are concluded outside the exchange. The buyer and seller can execute the transaction directly or involve a third party. The main hedging instruments are forwards and swaps. These transactions are one-time. They cannot be sold to third parties. OTC hedging is usually used to limit business risks.
By the size of the insured risks:
- full hedging – the size of the reverse transaction is equal to the volume of the first open position;
- partial hedging – the volume of the counter-trade is less than the size of the previously opened position.
By counterparty type:
- Buyer hedge . The investor insures the risks that are associated with a likely increase in prices or deterioration in the contractual terms of the contract.
- The seller’s hedge . In this case, risks are insured against a possible fall in prices or deterioration in the terms of the contract.
By the time of the transaction:
- Classic hedge . First, they draw up the main deal, then the insurance deal.
- Superior Hedge . Everything happens the other way around. First, they draw up an insurance deal, then the main one.
By type of underlying asset:
- pure hedging – the underlying asset in the main and reverse trades is the same;
- cross – the main position is insured by another underlying asset.
By type of hedging contract terms:
- unilateral – financial losses and income are borne by only one side of the transaction;
- bilateral – the division of profits and expenses falls on both sides.
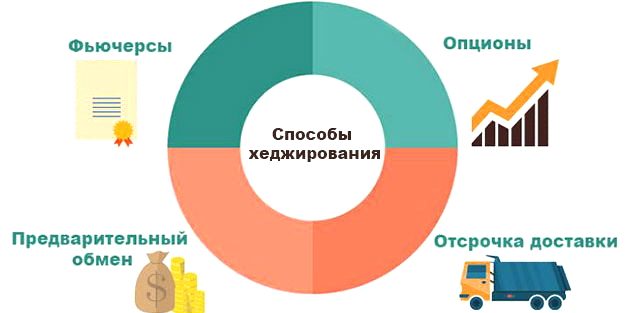
Hedging Instruments
The main exchange instruments for hedging are:
- Short position . In this situation, you borrow securities, sell them, and then purchase them at a lower rate. The difference between the selling and repurchasing price is the profit that will be made in a down market. Such trading is called margin trading. You trade in stocks borrowed. The broker will take a commission for the use of securities. It can also forcibly close a trade at an unfavorable rate for you if the position is not secured.
- Option . This is a contract under which the buyer can sell an asset at a predetermined rate. And it doesn’t matter what the price will be at the time of sale. If you expect a decrease in asset quotes, then buy a PUT option. Thus, you fix the price of the paper. In the future, if the shares collapse, then you can sell the asset at the original price. If quotes do not fall, then you have the right not to sell the asset.
- Futures . This is a contract for the sale of an asset on a specific date at a predetermined rate. If you think that the paper will become cheaper, then you sell a futures contract. On the due date of the contract, the other party will be obligated to buy the asset at a predetermined price.
- Swap . As part of a forward transaction, the parties exchange payments for a certain period. Such hedging is usually resorted to by fund managers. For example, the FinEx company when managing ETF funds.
- Inverse ETFs . Such funds are designed to mirror the benchmarks they follow. If the main index falls, then they rise. Inverse ETFs offer growth in 1x, 2x, etc. That is, trading with leverage is available.
Important! The above risk hedging instruments are available only to qualified investors.
In the over-the-counter market, a forward is used to hedge. This contract involves the delivery of the underlying asset. The terms of the forward contract are set by the parties themselves. 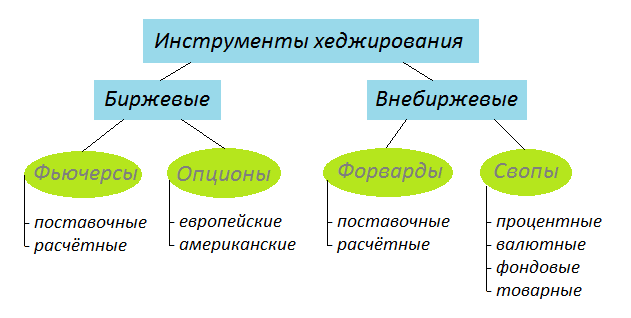
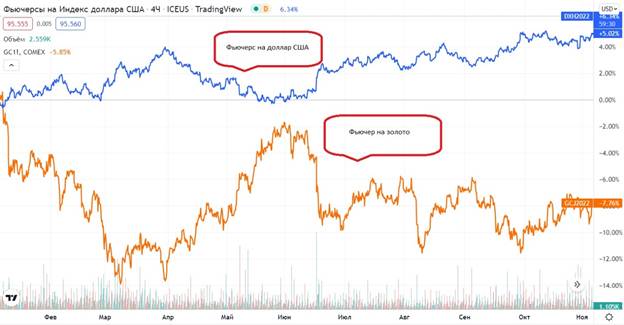
Hedging Example
The US dollar index and gold have a good inverse correlation. If an investor has gold in his portfolio, and he is afraid of a fall in the asset’s price, then he can hedge the risks through a futures contract for the US dollar index. This type of hedging is called cross hedging.
Mistakes when using a hedge
When hedging risks, inexperienced investors and traders sometimes make mistakes. As a result, they lead to the loss of part of the capital. The most common hedging mistakes are:
- the underlying asset was incorrectly selected during a cross hedge;
- erroneous conditions of the transaction are set;
- the wrong trading instrument for hedging is selected;
- no collateral for trading with leverage;
- the volume of the counter-transaction is incorrectly calculated.
Pros and cons
| Advantages | Flaws |
| A hedging strategy helps smooth out a fall in an asset’s price. | You need to pay commissions to brokers for making reverse trades. |
| There is an increase in the stability of portfolio income over a long distance. | Insurance doesn’t always pay off. Especially when cross hedging with different underlying assets. |
| There are no major drawdowns. The portfolio becomes more resistant to sharp fluctuations in quotes. | You can suffer serious losses in the event of exchange restrictions. For example, during margin trading with leverage or low liquidity. |
| Hedging strategies are applicable in the exchange market and in crypto trading. | There is an increase in the total number of transactions. Every open position has to be monitored. Otherwise, you can miss a good moment to exit. |
| All transactions are secure. | To access a wide range of tools, you need the status of a qualified investor. |
Hedging is a complex operation to reduce risks through the use of special tools. They are used only by professional market participants. Therefore, before making such transactions, understand the principle of operation of each derivative. This will not only save capital, but also diversify future investments.




