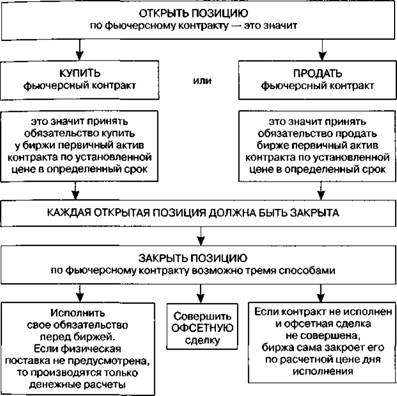
Use a futures contract to make transactions for the sale and purchase of a product or asset in the planned future at a fixed price. This obligation is how the given security differs from an option that gives the right to buy or sell, but is not forced to do so. Futures oblige both parties to the transaction to fulfill their obligations. At the same time, the material exchange of goods during such trading operations is not performed.

- What are futures and why are they used in the investment market?
- Differences between futures and options
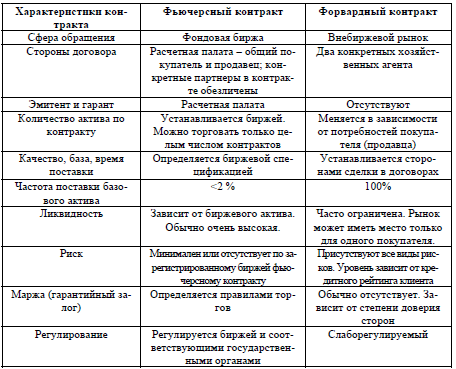
- Differences between futures and forward contracts
- Futures trading strategies
- Pros and cons of futures trading
- Types of futures contracts
- Futures contract price – contango and backwardation
- Insurance
- Expiration dates
What are futures and why are they used in the investment market?
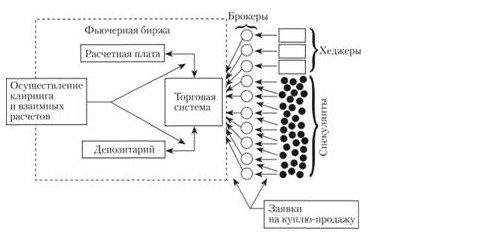
Futures contracts are used to establish the real market price for a particular instrument. They have certain applied value for investors:
- Speculative transactions that allow you to extract material benefits.
- Insurance against risks by hedging , which is interesting for suppliers and buyers of goods.
Futures are used in the commodity and commodity markets, they are characterized by the main parameters:
- The time of execution, namely the date on which the deal is scheduled.
- The subject of the transaction, in particular, raw materials, securities or goods, currency.
- The exchange on which the transaction is made.
- Units of quotation.
- The size of the margin.
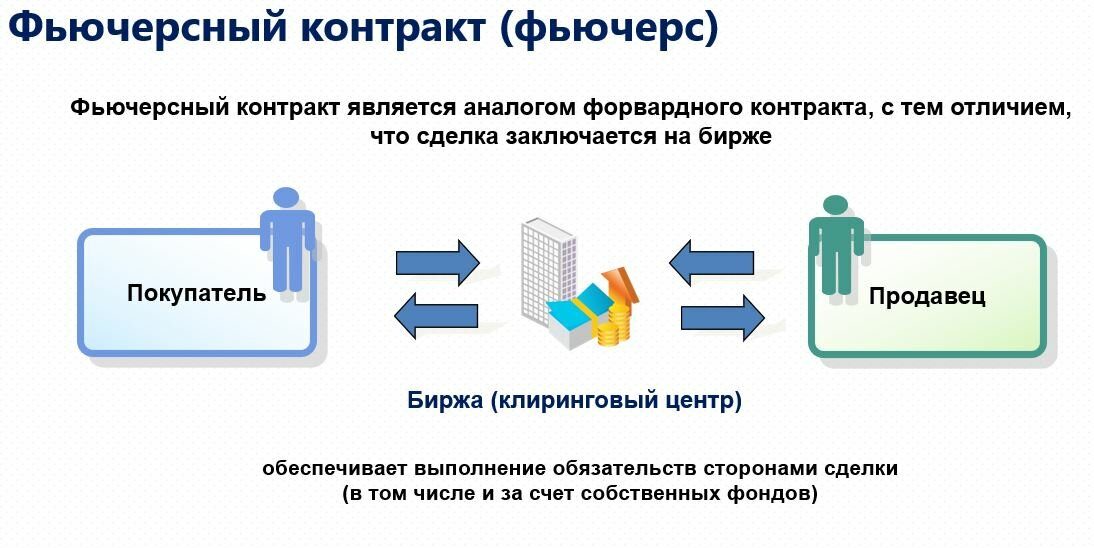
- Maintaining the balance of both parties to the contract.
- Replenishment of balance A and decrease of balance B.
- Replenishment of balance sheet B against the background of reduction of balance sheet A.
If the buyer’s account is replenished against the background of a decrease in the seller’s account, then the value of the instrument increases. That is, investor A could buy the product at a lower price and resell it at a higher price, thus deriving material benefits. In reality, the exchange relieves market participants from carrying out the necessary operations, calculations, immediately giving out the difference in real money to the party to the transaction. If the price has not changed, then the balance remains the same. The third scenario is realized if the price of the product falls, which was initially beneficial to the seller. Now it is possible to sell goods on more favorable terms, the current market price of which is less than the one that was specified in the contact. If we were talking about a real product, then the seller could buy it at market value and sell it at the price specified in the futures. The exchange, in this situation,relieves the parties from the need to transport real goods, but simply makes the necessary calculations and replenishes the seller’s account for a certain amount, which is the difference between the market value and the price specified in the contract. If one of the parties abandons the futures until the moment of its execution, then after the expiration of the terms specified in the contract, a comparison is made between the value specified in the document and the market price of the goods. then after the expiration of the terms prescribed in the contract, a comparison of the cost indicated in the document and the market price of the goods takes place. then after the expiration of the terms prescribed in the contract, a comparison of the cost indicated in the document and the market price of the goods takes place.
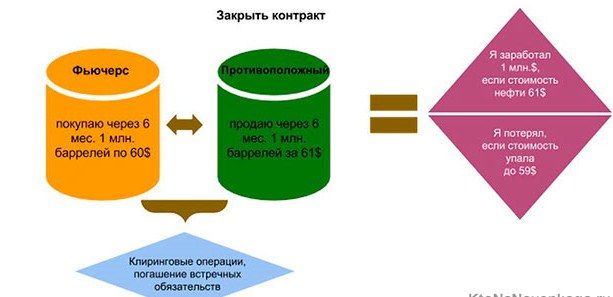
Differences between futures and options
Futures and options contracts differ among themselves by the obligations of the parties. This manifests itself during the expiration period.

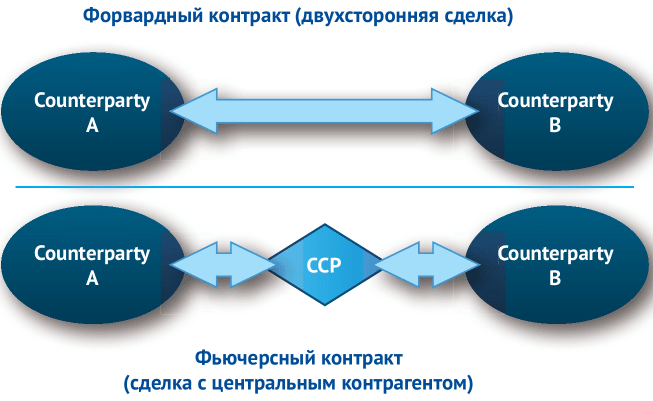
Differences between futures and forward contracts
Also, there are differences between forward and futures contracts, which are entered into by investors. A forward is called one-time transactions made outside the exchanges and assuming that the purchase of goods, securities or currency will occur in the future time. The parties discuss the main conditions in advance:
- price;
- terms;
- additional conditions.
In this case, the transaction is carried out with real assets, and not as with futures, when the transfer of goods is not involved.
The forward is intended to insure the participants in the transaction against price fluctuations that are likely to occur in the future. There are no strict standards when concluding a contract, so such transactions cannot be carried out on the exchange.
- goals – the forward will be concluded for the sale or purchase of real assets, which implies the consideration of all conditions favorable to both parties. In the second case, futures contracts are hedging their own positions or taking advantage of the price difference. Futures only in 5% of cases lead the parties to the exchange of real goods or financial instruments;
- asset volume – when concluding a forward contract, the parties to the transaction independently calculate the required volume, taking into account their needs. In the case of futures, the volumes are determined by the exchange, and market participants have the right to sell a certain number of contracts;
- quality of instruments – a forward provides an opportunity to use assets of any quality, depending on how requests come from the buyer. When it comes to futures, the quality of the instruments is determined by the specification of the exchange;
- delivery of goods – when signing a forward, assets are always delivered, and when a futures is concluded, delivery is carried out in the form established by the exchange, but in most cases it does not reach this at all;
- terms – the terms of delivery when signing the forward are determined by the parties to the transaction. The terms of futures contracts are determined by the exchange;
- liquidity – a forward contract is characterized by limited liquidity, since the conditions for its conclusion are acceptable for a certain range of counterparties, between whom it was concluded. Futures are highly liquid instruments, however, the level of this indicator depends on the quality of the underlying asset.
Futures trading strategies
To trade futures, traders use several popular techniques:
- the comparison of the exchange schedule of the contract with the next month for which the delivery is planned and the reporting period following it is carried out ;
- a comparison of the spot price for a share and a futures is carried out , if its value is higher, then we are talking about contango , which is considered a premium relative to the price of an asset. If the situation is reversed in the market, then it is called backwardation , which is considered a discount in relation to the base cost. It is on the exchange rate difference that arises in this situation that traders earn;
- studying the futures schedule using technical analysis, indicators, fundamental factors that can affect the price of the contract.
Trading by support levels:
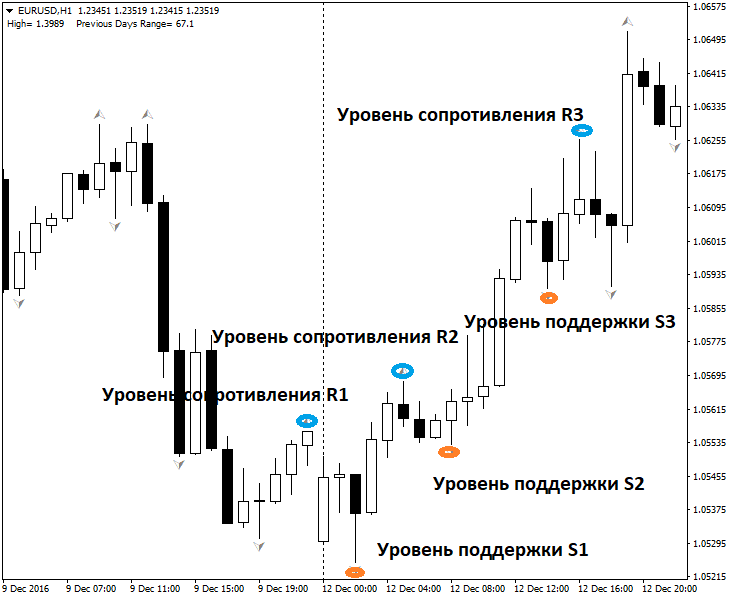
- temporal;
- spatial;
- calendar.
Pros and cons of futures trading
There are several advantages of futures trading:
- there are no additional costs and hidden commissions;
- there is access to a pool of futures with expiration for a year;
- high asset liquidity, volatility and dynamic trading.
Disadvantages of trading futures contracts:
- not suitable for long-term trading, as it is valid for a certain time;
- when expiration occurs, transactions are closed automatically, taking into account the current market price and deleting pending orders;
- you cannot transfer open trades to a contract expiring next month.
Weigh the pros and cons before trading these highly risky instruments.
Types of futures contracts
There are two types of futures contracts:
- Delivery.
- Settlement – without supplies.
Deliverable futures oblige the buyer and the seller to make the actual sale of the goods and pay for it within the terms specified in the contract. The settlement between them is carried out at the price that was fixed on the last day of trading. If with the onset of the due date the seller was unable to provide the buyer with the goods, then the exchange imposes penalties on him.
Estimatedfutures have nothing to do with actual deliveries of products. It is assumed that one of the parties will pay the second party to the transaction the difference between the value of the asset during the period of the transaction and the actual price of the product at the time of the expiration of the contract. Settlement between counterparties is made in cash, and physical delivery of goods is not provided. Such transactions are made for hedging or speculative manipulation. Hedging allows you to level out the probable losses incurred when entering into a contract in another market.
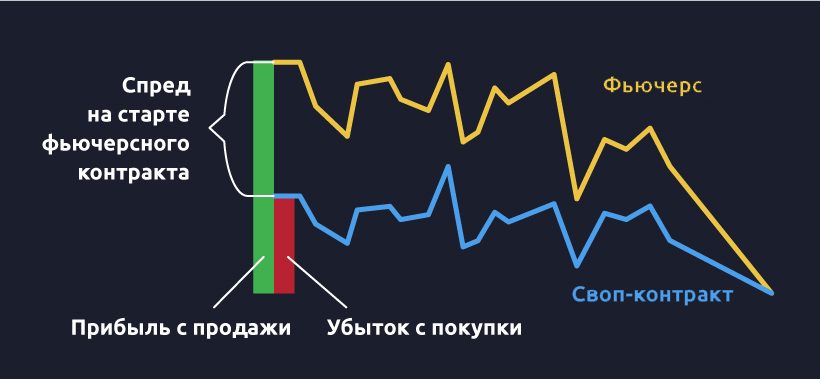
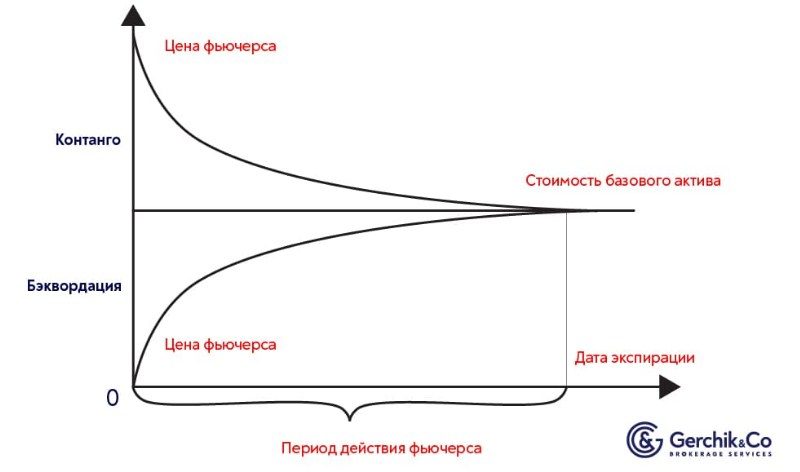
Futures contract price – contango and backwardation
A futures contract is categorized as an individual commodity with a value that differs from the price of the asset. This indicator may be influenced by forecasts and risks caused by a likely change in the subject matter of previously reached agreements. The price of an asset in the market and the value of a futures for this commodity can have a negative or positive ratio.
If a contract is more expensive than an asset, then this condition is called contango. In the case when the situation is the opposite, we are talking about backwardation.
In this situation, most investors hope that the price of the asset on the stock exchanges will soon significantly decrease.

Insurance
Trading is carried out on condition that the transaction is secured by means of a deposit, the size of which is 2 – 10% of the price of the contract asset. This is the insurance required by the exchange from both contracting parties. The set amount is blocked on the accounts, forming a kind of collateral. If the price of a futures rises, then the seller’s collateral increases, and if it decreases, it decreases. This mechanism avoids the payment procedure when concluding a contract. When a futures is held until it closes, the parties fulfill their obligations by supplying assets or transferring funds. When one of the participants does not want to fulfill their obligations, the exchange does it for him, leaving himself a certain amount of the guarantee. This scheme only works for contracts that provide for the delivery of an asset.
Expiration dates
There are several contract expiration dates. For example, for a dollar index, stocks, financial instruments, the expiration date is quarterly on the third Friday of the last month of the quarter. There are futures with a monthly output, in particular CME Crude Oil. Other types of contracts may end on other days. To trade futures productively, remember the expiration date of the contract. If there is an unexpected decrease in volume after the expiration of the next day of trading, then the deadlines are approaching, and most of the traders begin to close deals before the termination of the contract.


zur
Mani mlaif malaqa