What is a stop loss in trading in simple terms, how it works and how an order is placed – a stop loss order. Stop loss is an important financial tool for managing risks, and with them the loss of capital for traders. Its role is to set a predetermined maximum loss limit that the trader is willing to accept if things go wrong. All major
trading platforms allow you to set a stop loss, so there are few restrictions from this point of view. It is important to understand how to use it correctly, since inexperienced traders use it infrequently, while other investors may abuse it in positions where it should be avoided.
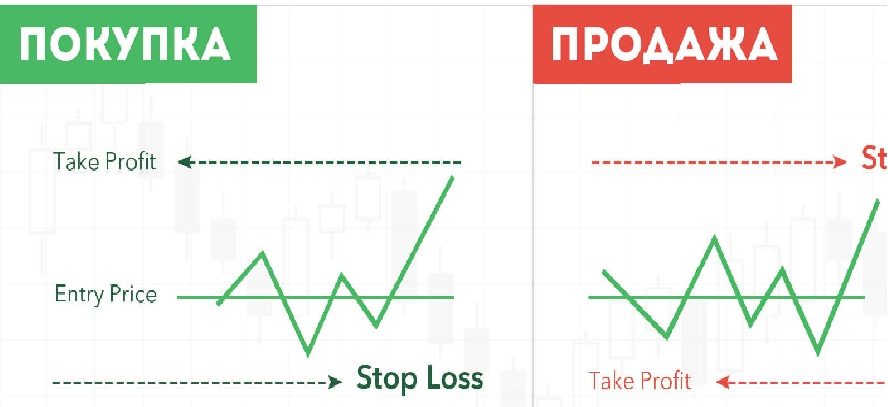
- What is stop loss, general concepts for beginners
- Stop Loss and Stop Limit – What’s the difference?
- Why do you need a stop loss in practice
- Where and how to place a stop loss
- How to choose the right stop loss and how to set
- Factors to Consider When Determining Where to Place a Stop Loss
- Setting a stop loss on Binance, Tinkoff
- What are the ways to set stops
- How not to set stop losses
- What is the best way to set a stop loss
- How stop loss works
- Stop Loss and Risk to Reward Ratio
- Set it and forget it strategy
- Stop Loss calculation for a limited period of time
- Carrying over stop loss to breakeven
- Removal of stops – how you can use it to your advantage
- Mental stop loss: advantages and disadvantages
What is stop loss, general concepts for beginners
No investor likes a loss in their portfolio. There are various hedging methods
that can be used to avoid losses, from complex operational strategies to diversification, but perhaps the easiest way to implement is stop loss. Its definition is intuitive. The term indicates the reached price level at which the trader automatically exits the market. In essence, a stop loss is, in simple words, an order to buy or sell, which will be executed only when the price goes against the transaction so much that it brings the maximum loss that the trader is willing to accept. That is, the transaction will be “cut off” before he incurs large losses.
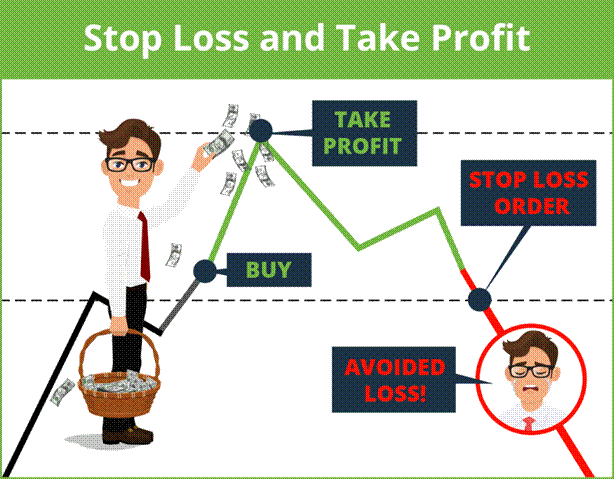
For example, a trader decides to buy a stock at a hypothetical price of 200 and sets a stop loss at -5%. This means that if the market goes in the opposite direction, the position will be closed with a loss of 10 (the price will fall to 190, the loss will be 5% of the investment amount, the investment will be closed by the broker).This is a very simple loss limiting system and is mainly used by traders who prefer technical analysis. They place stop orders either to limit risk or to protect some of the existing profit in a trading position. Stop loss placement is offered as an option through the trading platform on every trade and can be changed at any time.
- modulate risk capital in line with expected returns;
- avoid the common mistake of not exiting losing trades (when they say “sooner or later it will grow again”, and meanwhile losses are achieved);
- close profitable deals.
In practice, when a trader opens a directional position in a financial instrument, he decides to go long or short, at the same time he sets a price limit on the opposite side of the direction he is betting on, after which the position is automatically closed by the broker. The advantage of a stop compared to manually closing a position is that everything is done automatically. There is no need to be in front of a computer or smartphone with an open platform. As soon as the broker receives an instruction, he will follow it anyway. The concept is that it makes no sense to keep losing positions in the trading account indefinitely.
So, stop loss, what does it mean on the exchange? In financial transactions, stop losses “fix” the maximum amount of capital that a trader is willing to lose, based on a certain price level, below which he categorically does not want the stock to fall. When trading, in addition to specific goals and following a strategy, it is necessary to adhere to the rules of money management. Setting a stop loss is part of these rules. This is an automatic order that allows you to mechanically close a trade without making “subjective” decisions.
Stop Loss and Stop Limit – What’s the difference?
The stop order becomes a market order only when a certain price level (previously specified) from the market price is reached. It can be used both to enter a new position and to exit an existing position. There is a difference:
- Sell stop losses protect long positions by activating a market order to sell if the price falls below a certain level. The stop sell price is always below the current market price. This strategy is based on the assumption that if the price falls this low, then it can continue to fall even further.
- Buy stop losses are conceptually similar, but are used to protect short positions. The stop price is above the current market price and will be triggered if the price rises above that level.
Stop limit orders are similar to stop losses. But, as the name suggests, there is a limit to the price at which they will be executed. Two prices are specified – a stop price, which converts an order into a sell order, and a limit price. Instead of becoming a market sell order, it becomes a limit order that will be filled at a certain or better price level. Difference:
- A buy limit order tells the broker to only buy if the price reaches or below a specified level.
- With a sell limit order, the broker is instructed to sell at the market value only if it reaches the specified level or higher.
For example, the stock will not fall to the stop loss price, but will continue to rise, eventually reaching $50 per share. The trader cancels the stop loss order at $41 and places a stop loss at $47, with a limit of $45. If the share price drops below $47, the order becomes a limit order. If the share price drops below $45 before the order is filled. It will remain unfilled until the price returns to $45.Many investors remove stop limits if the price of a stock falls below the limit price, because they place them solely to limit losses when the price has fallen. Since they have lost their exit opportunity, they are waiting for the price to rise. An effective application of a limit order can be to predict the profit that the trader intends to make before closing the position. For example, if a buy position is open, you can use a sell limit order at a certain level (a certain number of points above the current one), which automatically closes the position when the price rises (thus earning these points).
Why do you need a stop loss in practice
A priori, a trader does not know whether his forecast will be confirmed in the market, so he sets a price limit, which protects him in case the market moves in the opposite direction to his trade. The main purpose of a stop loss is to close a position at an expected loss in accordance with the trader’s trading plan and strategy. It is clear that behind the opening of a position in one direction or another (long or short) there is an analysis (technical or fundamental) performed by the trader. Any strategy implemented in the financial markets, statistical or not, has results on a fairly wide range of operations, which can be both positive and negative. https://articles.opexflow.com/analysis-methods-and-tools/osnovy-i-metody-texnicheskogo-trajdinga.htm Financial markets are impossible to predict and any trader, regardless of his experience, may be on the wrong side of the road. Thus, stop loss is a useful tool for all financial market operators. The best action is to provide a safety mechanism that is applied in case the desired direction of the transaction turns out to be wrong, and the trader has limited the maximum potential loss.
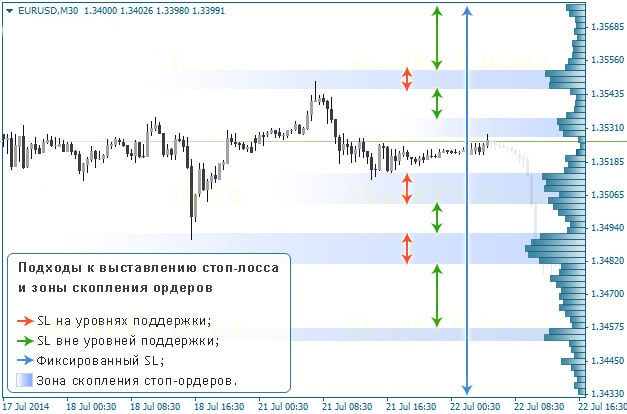
Where and how to place a stop loss
First of all, it depends on the risk threshold of the trailer – the price should minimize and limit losses. Stop loss is placed on speculative positions, such as when investing through a
contract for difference (CFD) and when using leverage. This is because speculative positions tend to be based on a prediction of where the price will go in the short term.
Conversely, when investing in the long term, this tool is less profitable. In fact, in most long-term investments, it does not make sense to use it.
The reason why it is important to use a stop loss in day trading has to do with financial leverage, which is typical for short-term investments and
scalping . With leverage, also called “margin investing”, a trader borrows money from his broker to buy financial instruments. This increases the fluctuations of investments, because the more you invest, the more profit you get and the more you lose.
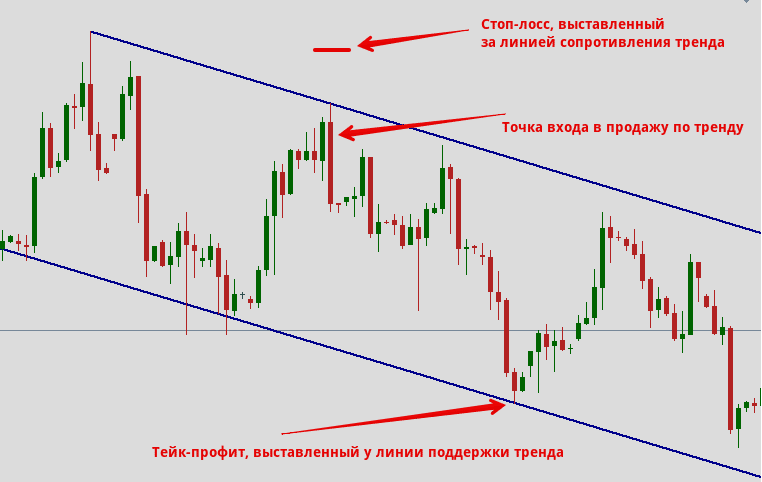
How to choose the right stop loss and how to set
There are basic rules that suggest setting a stop loss wisely and profitably.
- Choose the exact entry price . Never open a trade at a random price, but study the entry price and enter the market only at this point. Thus, a stop loss can be placed a short distance from the entry point, where prices can only come if the market analysis was wrong. Thus, the order allows you to exit with little damage, re-analyze the market, the situation and, possibly, return at a better price.
- Define stop loss . You need to decide in advance how much capital to risk (in pips or money). It is important that the stop loss is below the expected profit from the trade, in other words, the loss exit price should be closer to the market entry price than the profit exit price.
- Make a trading plan before the operation . Analyze and pre-select entry and exit prices for both loss and profit. Each transaction needs to devote some time to study, analyze the state of the market.
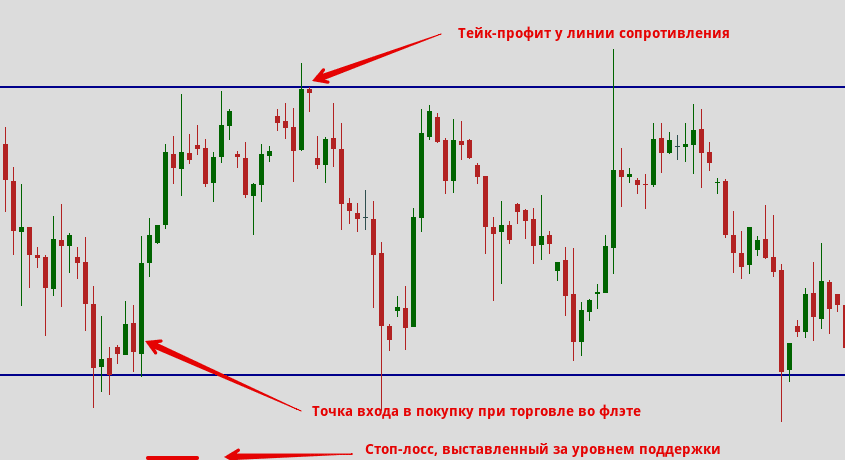
The hardest thing for a trader is to admit defeat. If an investment does not go as expected and hits a stop loss, you should calmly accept it. A big mistake is when a trader moves the stop loss so that it is not affected by the price if something goes wrong.
Factors to Consider When Determining Where to Place a Stop Loss
Stop loss positioning should actually follow logic. The stop loss point should be the point at which the original trade idea (the one that prompted the trade) is no longer valid. Setting a stop loss that is too low threatens the trader with a loss of chances to get a good result, since most trades will be closed before they can make a profit. Obviously, setting a stop loss that is too high also has negative consequences, as the expected losses can be excessive.
Setting a stop loss on Binance, Tinkoff
Binance has an order option called OCO (One Cancel the Other) that allows you to set take profit and stop loss strategies at the same time. In fact, only one of them will be executed. As soon as one application is partially or completely executed, the remaining one is canceled.
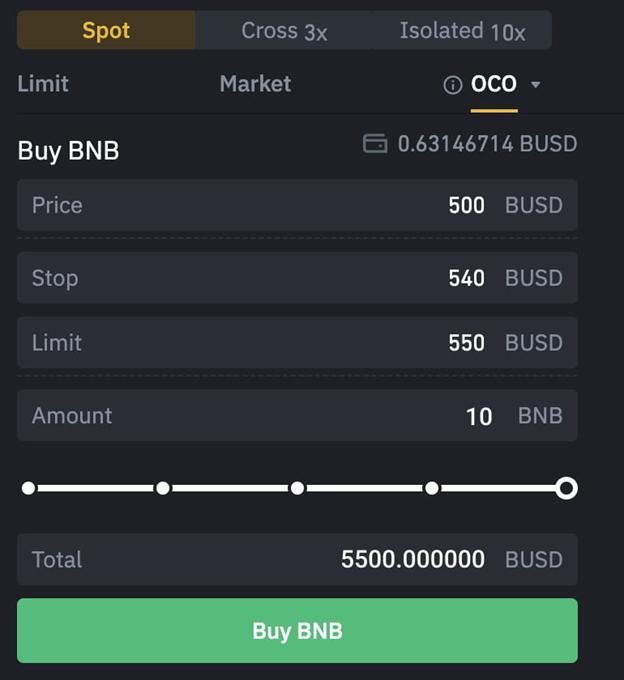
- Price where the take profit price is indicated
- Stop, which indicates the level of stop loss activation
- Limit – the real price of the stop loss
Why stop and limit? Because the price doesn’t actually appear on the book until the stop is hit, at which point the price enters limit mode where it will then be executed. For this reason Limit is below Stop. Obviously, the inverted parts maneuver is also functional for trading short (margin). In this case, the values will be reversed, since the profit will have a lower price, and the stop will have a higher one. Another method assumes that the trader has already entered the market through a previous purchase. However, it is also possible to take advantage of OCOs at this stage. Suppose the market situation is not defined. Thus, it is possible to set the purchase price at a low level, perhaps in order to intercept the rebound. However, if this does not happen, it may happen that the price literally “explodes” upwards. In this situation, it is clear that by entering higher, you will earn less, but at least you will be in a full rise. In any case, you can take profit from the terminal part of this event.
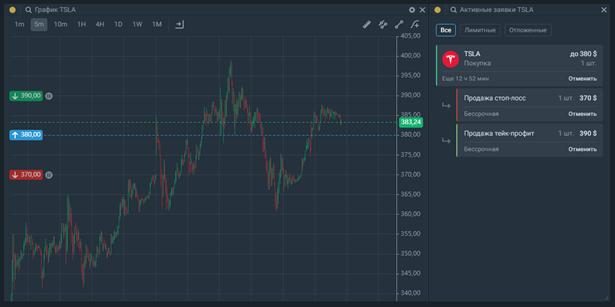
Tinkoff Investments , it is possible to set two stop orders – take profit and stop loss. Required:
- Go to the Investment tab → Catalog → select the desired function. In the stop loss/take profit field, click +Add. Then (in the upper right window) turn on the Requests toggle switch.
- Specify a price or stop order.
- Specify the number of lots (buy or sell).
- Click on Expose.
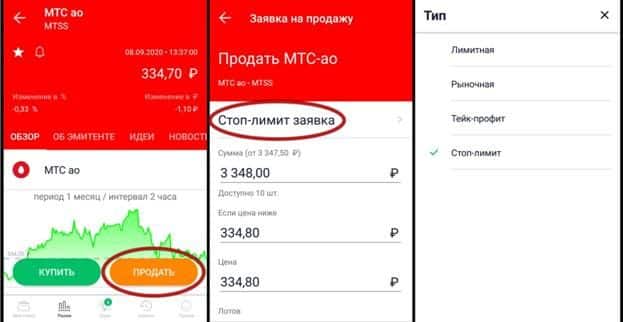
Sberbank Investor application is called stop limit. Let’s say we’re talking about a sale. We select the desired asset, click on the sell button, a page appears in which we indicate the desired function. Buying is the same. How to put a stop loss:
- Click on the raised fingers icon with the letter S.
- A window will open where you can set the stop loss execution parameters.
- Specify the order activation condition (sell, buy).
- Choose a stop loss strike price (below the entry price for a long position, below the entry point for a short position).
- Set the price at which the order is placed (the safest option is “at the market price”).
What are the ways to set stops
We can definitely say that when a trader decides to open a stop loss, he is ready to risk some amount of money on this transaction. Of course, cutting losses is a skill that traders learn over time if the goal is to achieve high success. Any trader who decides to enter the market knows with certainty when to enter and exit a trade, even before opening a position in the trading platform. There are various criteria for placing a stop loss, although there is no one-size-fits-all or best way. It is important to understand the risk you are taking by choosing this position. Technical traders look for ways to time the market, and stop losses and stop limits are applied differently depending on the type of timing methods being applied. In some cases, universal placements are used, such as 6% trailing stops on all securities, in others, they are stock or pattern specific, including average percentage stops of the true range. Stop loss types based on:
- in percents;
- in monetary terms;
- by candlestick patterns and graphical figures;
- by technical levels (static and dynamic support and resistance);
- by volatility (using the ATR indicator).
https://articles.opexflow.com/analysis-methods-and-tools/yaponskie-svechi-v-trajdinge.htm For the percentage method, the best stop loss position is determined based on the amount of capital that the trader is willing to risk on each trade. It implies an exit from a position after the underlying asset has changed against the direction by a predetermined percentage. Experienced trailers advise not to invest more than 2% of the capital for each trade. Money Stop Loss – An order type based on the money loss incurred on a given trade. For example, a trader may decide to close a position after suffering a predetermined monetary loss. Based on Candlestick Patterns and Chart Patterns – Those invalidation levels based on the location of specific candlestick patterns, or reversal or trend continuation patterns. https://articles.
support and resistance levels to determine the most appropriate level that will invalidate the current trade. These can be horizontal or dynamic supports for bullish strategies, static or dynamic resistance levels for bearish strategies.
A stop loss based on
volatility can be considered the most “safe”. Placing an order based on volatility allows prices to “breathe”, avoiding premature stops due to temporary adverse price movements.
How to calculate and set stop loss, take profit, trailing stop and partial closing of positions: https://youtu.be/s8K2NIXhaaM
How not to set stop losses
The main problem with stop losses is that they work in the wrong direction. When stocks go down, they become the best investment. Return on equity is directly related to how cheap a stock is. Other things being equal, the cheaper the stock, the higher the potential return. Setting a stop loss means deciding not to sell the stock now, but to sell it when the expected return is higher than it is now. It doesn’t make any sense. Instead, limit orders can be used. By setting the stop loss level too far, the trader risks losing a lot of money if the financial instrument goes in the wrong direction. Alternatively, by setting the stop loss level too close to the buy price, the trader loses money as they are taken out of trades too early. A fixed or hard stop loss is placed without adjustment at the time of the trade. It is set at the opening of a trade and kept there (or sometimes moved up to break even when the market goes against the trader). The basic idea is that the stop loss is not market responsive, it is allowed to run until the trade is closed. But given that every financial asset moves differently over time, this is a bad idea.
What is the best way to set a stop loss
Is there a better way to place a stop loss? No, as it depends on the analysis that goes into the market. Experts tend to believe that the ideal stop loss should be around the 3:1 level. For example, a trader wants to make 300 pips and sets a stop loss at 100 pips from the chosen entry price. However, there is no definite and absolute technique. The stop loss point should be considered as the “point of invalidity” of the trade idea from which the trader opened the position. Therefore, when the price reaches a point, it means that it is better to get out of the position so as not to make more losses. The stop loss must be sustainable, or the loss must not significantly affect the capital available for trading. As a rule, for one transaction, it is considered acceptable if it is 1-2% of available capital. Some recommend higher percentages, 5–7%. But it depends on how much the trader is willing to take the risk. In any case, it is important to apply a trading strategy of a certain efficiency. The stop loss must also be “smart”, that is, located at strategic points on the observed chart. In principle, it should be below (for long) or above (for short) important market swing points. This leaves prices with a “little breathing room”. In other words, you should leave some space between the previous high or low and the stop loss level. The distance from the critical swing points should be set taking into account the volatility of the instrument with which the trader is working. Placing a stop at different points on the chart for the sole purpose of reducing risk increases the likelihood of it being triggered, resulting in the exit of the position and then for prices to hit the target, set by the trader. This is a consequence of the so-called market noise. Another consideration a trader should take into account when deciding on a stop loss size is to accept it calmly. Otherwise, there is a risk that the trader, overcome with anxiety, will close his position even earlier. That is, even before the actual achievement of the set stop loss.
How stop loss works
The conceptual functioning of this tool, closely related to its usefulness, is relatively easy to understand, especially when put into practice. Theoretically, the work of a stop loss is in the following aspects:
- The central order is what the stop-loss convention is worked out on. This can be thought of as buying Gazprom shares, a micro lot of gold, or alternatively an ETF. These are instruments that can increase or decrease in value after purchase.
- The trend can be up and down . Stop loss is set wherever a loss is expected. If you fix it as a share of the profit, it would be a take profit.
- The stop loss is triggered automatically if and only if the order condition is met .
- A stop order is usually placed at the resistance level , or rather, a little lower, in order to avoid further losses in the absence of a rebound.
How stop loss works on Binance: https://youtu.be/BJIZI-8KtBM
Stop Loss and Risk to Reward Ratio
When people talk about stop loss, they also mean the ratio of risk to reward. This is a stop loss that takes into account the variable risk to reward ratio and correlates the amount of expected profit with the amount of expected losses. Therefore, the higher the risk reward ratio, the more desirable this type of trading will be. For example, a trader decides to buy shares at a price of $5, and the forecast says that the profit on them will be $10. This means that the share price could rise to $15. In this case, the stop loss will be set at $2.50, i.e. 50% of the capital invested to achieve a profit of $10. This means the risk to reward ratio will be 10:2.5 or 4:1. (numerator – profitability, denominator – risk).
Set it and forget it strategy
Whether stop losses are used purely for safety or as an integral part of a strategy, there is debate among traders as to whether a fixed (hard), trailing (trailing) stop, or a combination of the two is better. The reality is, as with most things, it all depends on the circumstances, each type of order has its pros and cons. Some of the advantages and disadvantages are specific to a particular trading style, others are general. A hard stop loss has the benefit of a “set it and forget it” feature. The trader does not monitor the market for as long as the trade is open. First of all, if the operator is focused on setting stop losses at resistance levels, which, as a rule, remain static due to the accumulation of orders at a certain point. Trailing stop reacts to market conditions, that is, as the market changes, so does the stop. It is important to note that this is not just a stop loss movement after a trade is entered, it means that it works according to some pre-defined criteria and trading strategy.
Stop Loss calculation for a limited period of time
The principle of stop loss based on a predetermined time period corresponds to trading signals using high volatility moments. This is a rather complicated method. If only because it takes into account the technical analysis indicator and puts it at the center of the process of determining the stop loss. At the theoretical level, there is nothing incomprehensible or ambiguous: the stop loss is placed immediately after the price range drawn by the fluctuations. Simply put, a stop position means “out” of volatility. Obviously a little further, just a few pips. The basic principle is more than logical. If the price stays within the “physiological” fluctuations for a given period, then the price can reverse course in the short term, making the trade always recoverable. Since a stop loss allows you to exit the market when the situation is no longer recovering, obviously that the price level should be set beyond the volatility. However, the problem remains – how to determine volatility? You need to use technical analysis. So, ultimately, this method uses indicators. He has practically no flaws. It intervenes when the trade is truly irrevocable, as supported by technical analysis, but is difficult to practice. First, you need not only to be able to read, but also to set the indicator correctly. Secondly, it is necessary to be able to distinguish between false signals, to avoid false interpretations. when a trade is truly irrevocable, this is confirmed by technical analysis, but it is difficult to practice. First, you need not only to be able to read, but also to set the indicator correctly. Secondly, it is necessary to be able to distinguish between false signals, to avoid false interpretations. when a trade is truly irrevocable, this is confirmed by technical analysis, but it is difficult to practice. First, you need not only to be able to read, but also to set the indicator correctly. Secondly, it is necessary to be able to distinguish between false signals, to avoid false interpretations.
Carrying over stop loss to breakeven
Breakeven is the point at which the trader does not incur losses, but also does not receive any profit. Moving your stop loss to breakeven can be either a good decision or a bad decision, it all depends on the circumstances. Most of those who trade in the financial markets claim that they do it to protect their capital. It is possible to move the stop loss 10 pips higher, or 10 pips below the entry price, but traders still prefer to move it to the exact entry price. In fact, the motive is fueled more by the fear of losing than by the desire to win. This psychology of not wanting to risk loss for profit is destructive (usually resulting in too early exclusion from a potentially profitable trade), under such conditions it is not easy to become a successful trader. The whole premise of a stop loss is to take the trader out of the trade, if the market cancels the setup. This usually involves breaking a key high or low, what the operator defines as critical (for a trade setup). A stop loss placed at the entry price does none of this. Of course, this protects capital, but hitting a break even stop doesn’t invalidate the setup because the market doesn’t know where the trader has entered. Price action trading works because market participants from all over the world see the same formation in real time. The bull flag pattern usually breaks higher because enough traders see the same pattern and know that this means that higher prices are likely when resistance is broken. 
Removal of stops – how you can use it to your advantage
The term “running stops” is used by traders whose stops hit exactly at the low of the move, and then the stock immediately began to move up without them. They believe that market makers “carried them out of the spot.” As stops are posted to the exchange, market makers can see them on everyone and supposedly manipulate the stock price on occasion to trigger a large number of stops and get shares.
In fact, blaming others is an excuse that traders make up for themselves whose stops were hit, after which the price moved in the direction of their position. This conspiracy theory defies logic. The market is an auction. In the absence of liquidity, the market maker creates the market, he also determines the bid and offer price.Anyone who comes in with an order with price movement (up bid or down ask) becomes a market on that side. If the financial asset is liquid, there may be hundreds or even thousands of orders in the order book in close proximity to the current price – and each order is for 100 or 1000 shares. The trader places a stop order $2 below the current price and assumes there are 50,000 shares in the order book between them. It is strange to believe that the market maker is going to sell 50,000 shares in order to lower prices by $2, remove the stop and then reverse the market. And all for the sake of a particular trader. Narrow stops often work. Broader ones don’t, and sometimes stocks just drop to where the stop was placed. In any case, the responsibility for losses lies with the trader. It is important to understand and accept this,
Mental stop loss: advantages and disadvantages
An inexperienced trader starting a trading or investing venture discovers many things that need to be learned and understood before being used as strategies in order to be successful. Stop loss is one such useful tool in many trading programs. But they use it in different ways, trying to achieve the same goal – profitability. Hard is the most commonly used approach when it comes to limiting losses. This is a simple setup and a reassuring method for many operators, ensuring that if the price goes for an unexpected or extended drop, the position is automatically stopped and held at a certain level until the bottom of the drop. The downside is that often the price bounces back in the trader’s favor after hitting the stop. Ultimately, the losses are wasted. But it’s important to say that a method cannot be called right or wrong. The question is what is more convenient for a trader. Institutional traders use a mental stop loss, a method in which a stop loss is mentally determined and executed manually as soon as a price level is established at which the operator decides to sell the financial instrument, based on short-term or long-term profit. However, it requires expert skills and a high tolerance for risk, in addition to full commitment to the original solution. Institutional players have certain trading strategies, mostly long-term, well trained and experienced. They do not use any leverage and can afford to cover wider fluctuations than the average trader. The advantage of this type is that the trader has absolute control over the stop. If the price does not move to a predetermined stop, the veteran trader may choose not to place it until he receives stronger confirmation. This results in floating drawdowns and uncut trades. The trader stays in the game and has a chance to return to profitability. It gives the trader a lot of flexibility that suits their trading style to make adjustments to changing market conditions. But it requires a deep understanding of price action to be able to properly exploit this flexibility. The disadvantage is that this type requires constant monitoring of the market, the trader must always be aware of his transactions. The trader stays in the game and has a chance to return to profitability. It gives the trader a lot of flexibility that suits their trading style to make adjustments to changing market conditions. But it requires a deep understanding of price action to be able to properly exploit this flexibility. The disadvantage is that this type requires constant monitoring of the market, the trader must always be aware of his transactions. The trader stays in the game and has a chance to return to profitability. It gives the trader a lot of flexibility that suits their trading style to make adjustments to changing market conditions. But it requires a deep understanding of price action to be able to properly exploit this flexibility. The disadvantage is that this type requires constant monitoring of the market, the trader must always be aware of his transactions.
Beginners are encouraged to use hard stops, at least until they can control their emotions and discipline. In addition, it is important to have a good understanding of the market before making quick and objective decisions in real time.
Each type of stop (mental and hard) has its advantages and disadvantages, but they should be viewed as a kind of insurance that protects capital from serious damage. This is a difficult decision, only through trial and error, assessment of personal qualities or weaknesses can one determine which is better. The biggest obstacle to mental stops when trading is indiscipline. Many fail to cope with fast market action, a losing situation, failing to focus on a trading plan before a trade. This leads to blurry decisions that make it difficult to stick to the original mental stop. In many cases, it turns out to be very far from what was originally planned, which leads to a larger loss than expected. The mental stop encourages the trader to focus on the trade, without being distracted by anything else. If the hard “relaxes”, the mental one is based on concentration and attention, otherwise you can miss important information that follows between transactions. Trading should be taken seriously. The moment concentration is lost, everything is out of control. There are quite a lot of traders who do not use any stop loss methods. But to work without a stop, you need to have strict guidance on alternative risk management. This is usually due to very low leverage (or even negative). The plan also includes a price action condition to shorten the trade (a form of mental stop). when concentration is lost, everything gets out of control. There are quite a lot of traders who do not use any stop loss methods. But to work without a stop, you need to have strict guidance on alternative risk management. This is usually due to very low leverage (or even negative). The plan also includes a price action condition to shorten the trade (a form of mental stop). when concentration is lost, everything gets out of control. There are quite a lot of traders who do not use any stop loss methods. But to work without a stop, you need to have strict guidance on alternative risk management. This is usually due to very low leverage (or even negative). The plan also includes a price action condition to shorten the trade (a form of mental stop).



