Open Source is software that is licensed under open source standards. The principle of openness covers not only the sphere of software development. For example, designers provide access to free templates and fonts. In some countries, government agencies are switching to open source software. In Germany, the city of Munich has decided to switch to the LiMux operating system, which is a customized version of Ubuntu. In Hamburg, officials decided to use the Phoenix office suite instead of Microsoft Office. UK government switched from PDF to ODF. In France, the gendarmerie uses the Ubuntu OS and the free LibreOffice.
- Requirements for open source software
- Open source projects – what is their feature
- The history of the emergence of free software
- Open Source Licenses
- Examples of open source projects
- How to get involved in an Open Source project
- Using Open Source in the Development of Trading Robots
- GEKKO bot
- Zenbot
- OsEngine
Requirements for open source software
Let’s list the main requirements that an application distributed under the Open Source license must meet:
- programs are distributed free of charge;
- The software comes with source code, if it is not in the basic kit, then you can freely download it or get it in another way;
- the code can be changed and parts of the code can be used in other projects, and the modified applications should be redistributed under the terms of the Open Source license;
- discrimination of any groups of people is not allowed, for example, in the USA there are restrictions on the export of programs, but a free license cannot establish its own prohibitions;
- The Open Source license permits all uses of the applications, so the developer’s personal moral convictions do not interfere with distribution, for example, clauses such as: “it is prohibited to use for genetic research” are unacceptable;
- all rules related to the Open Source license are the same for all users, additional agreements such as nondisclosure are prohibited;
- the license cannot be tied to the program, the developer using only a part of the code has the rights that the full product gave;
- the user can choose what he will use, for example, it is forbidden to require that the software supplied with Open Source be open source.
Open source projects – what is their feature
Most applications distributed under the Open Source license have the following differences:
- programs are written by those who use them, therefore, developers monitor the code, quickly fix errors and discovered vulnerabilities;
- most of the products are compatible with several operating systems;
- the Open Source developer community is open to contact users who can submit their suggestions;
- usually updates for free software are released more often than for commercial ones, therefore, errors are eliminated faster;
- users, if desired, can support the application they like with money;
- The risk of infecting a computer or smartphone when installing an Open Source program is minimal, since they come with the source code.
The history of the emergence of free software
The founder of the free software movement is believed to be Richard Stallman. While working at the Artificial Intelligence Lab at MIT, he contributed to the development of free software. For example, in writing a text editor EMACS for PDP computers. In 1984, Stallman quit his job at MIT and founded the GNU Project. Its enthusiasts coined the term “free software” and developed the GNU manifesto.

Open Source Licenses
There are several different Open Source licenses. To make it easier to understand them, we provide the following figure, which shows how they differ from each other.
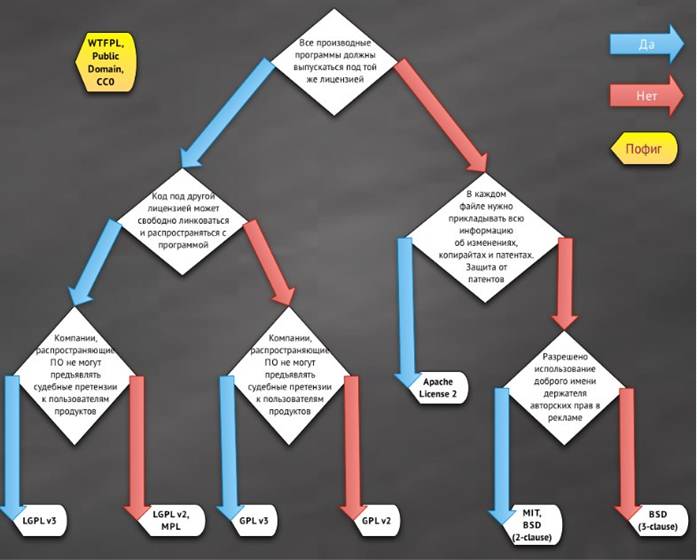
- The MIT license was developed in one of the leading educational institutions in the United States – Massachusetts Institute of Technology. It almost completely coincides with the three-clause version of the BSD license, with only one clause added, which prohibits the use of the author’s name in advertising. Under it came out: XFree86, Expat, PuTTY and other products.
- The BSD license first appeared in the early 80s of the last century to distribute the operating system of the same name. There are the following options for this license:
- The Original BSD license is the first original license, also called a four- clause license.
- The Modified BSD license is a three-clause license, it excludes one clause that requires advertising to indicate that this application uses software developed at the University of California.
- Intel license that was developed for patent-protected applications. It is not supported by the Open Source Initiative.
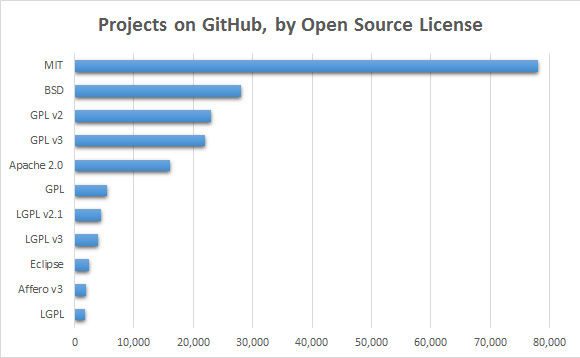
- The GNU General Public License is the most popular license. She appeared in 1988. In 1991, an improved version of GPL v2 appeared, which has not lost its relevance to this day. In 2006, the GPL v2 license was adopted.
- The GNU Lesser General Public License, or GNU LGPL for short, was created to link libraries with software distributed under other licenses.
- The Apache license allows you to modify and redistribute programs in both source and binaries. In addition to the rights to the product, the transfer of patents is also envisaged.
- Guile is similar to the GNU GPL, but it adds a clause that permits open source and nonfree software to be merged, so it cannot be considered a strict copyleft, but it is nonetheless compatible with the GNU GPL.
- The Common Public License was developed by IBM for its development. It allows you to change the code and use it in commercial programs. This license was used by Microsoft for Windows Installer XML.
- The Mozilla Public License (MPL) is a complex license that is not strict copyleft.
- License of Sun Publi c License similar to the MPL, but there are minor changes, for example, instead of Netscape listed Sun Microsystems.
There are also other less common licenses such as Guile, Common Public License, Mozilla Public License, and others. https://youtu.be/oAW5Dh9q3PM
Examples of open source projects
The development of the Linux kernel and GNU applications became the basis for other Open Source applications. The arrival of Netscape has attracted the interest of large IT companies. Since then, many different products have been developed. Let us first mention Debian, which supported the Free Software Foundation from 1994 to 1995, and later the Software in the Public Interest non-profit organization was created, which continued to fund the project. Within the framework of this project, not only the operating system was created, but also the office suite LibreOffice, the Firefox browser, the Evolution mail client, the K3b CD burning application, the VCL video player, the GIMP image editor, and other products. The Apache Software Foundation, a non-profit company, emerged as an Open Source software support project.The most popular product of this organization is the web server of the same name. The company now supports a large number of projects distributed under the Apache license. ASF sponsors include Microsoft, Amazon and Huawei. Another open source company is Red Hat. The main development of which is an operating system based on the Linux kernel. She is engaged not only in software, but also in technical support and training of specialists. It was acquired by IBM in 2018. Google also develops free software. She develops and supports the following projects: the TensorFlow library for developing machine learning systems, the Go language, the Kubernetes program for automating software deployment, and other products. In science, Open Source concerns not only software, but also the publication of works,peer review and support of educational resources. In 1991, Paul Ginsparg organized an electronic archive arXiv at the Los Alamos Laboratory, in which one can find works not only in physics, but also in medicine, mathematics and other sciences. CERN also has a portal with open scientific works.
How to get involved in an Open Source project
If you want to practice programming and fill up your resume, then participating in the development of an Open Source product is exactly what you need. We will tell you in stages what is needed for this. First of all, you need to register on GitHub and select a project in which you will participate. It should be of interest to you. It’s good if it contains a lot of tasks that you can do. You should also pay attention to the popularity of the project, it can be determined by the number of stars. It is also important to determine how active the development is and when the last changes were made. After choosing an interesting project, you need to find a curator and establish interaction with him. The next step is to select a task. To begin with, it is recommended to choose the simplest task. The main thing is that you can solve it.After that, transfer the project to your place and install all the necessary tools. After you have solved the problem, make suggestions for changing the code in the repository. To do this, you need to upload your code to GitHub and click the “Pull request” button. After that, you will need to enter the name of your request and a description. After that, you need to wait for the curator to accept or reject the proposed changes. If, after taking on a task, other urgent matters appear, or you realize that you will not be able to cope, then you can refuse the task. This is normal, but you need to communicate your decision to the curators.After that, you will need to enter the name of your request and a description. After that, you need to wait for the curator to accept or reject the proposed changes. If, after taking on a task, other urgent matters appear, or you realize that you will not be able to cope, then you can refuse the task. This is normal, but you need to communicate your decision to the curators.After that, you will need to enter the name of your request and a description. After that, you need to wait for the curator to accept or reject the proposed changes. If, after taking on a task, other urgent matters appear, or you realize that you will not be able to cope, then you can refuse the task. This is normal, but you need to communicate your decision to the curators.

Using Open Source in the Development of Trading Robots
A trading advisor or
robot is a program that makes transactions on the exchange according to a predetermined algorithm. They can trade either completely independently or in a semi-automatic mode. In the second case, they simply send signals about the trade, and the trader makes the final decision. Let’s list the advantages of trading robots:
- The trader does not need to keep track of prices himself.
- Expert Advisors operate strictly according to a given algorithm, they have no emotions.
- Robots react much faster than humans.
But besides the pros, automatic advisors also have disadvantages:
- in a non-standard situation, for example, with a sharp jump in the rate, the advisor may react inappropriately, and the trader will lose money;
- some professional advisors have to pay a subscription fee.
Next, let’s take a look at a few Open Source trading advisors. They can be downloaded from GitHub, installed and used for trading. You can also improve the source code and create a robot for yourself.
GEKKO bot
This is a proven advisor that appeared many years ago. Many traders started trading with this robot. It is not currently supported by its creators, but it is available for free download from GitHub. It can be used on crypto exchanges, it can collect market information and place orders. GEKKO bot has many settings, with which you can test the trading algorithm, as well as adjust and optimize the system for making deals. It has a set of ready-made strategies that you can customize. It is also possible to create your own trading system. It supports 23 exchanges, including: Bitfinex, EXMO, Bittrex, Bitstamp.
Zenbot
The Zenbot cryptocurrency trading advisor uses artificial intelligence for trading. It is possible to customize it according to your wishes. It is compatible with most operating systems. Can make high-frequency trades, trade multiple assets at the same time. In addition, this bot can make money by arbitrating cryptocurrencies. But it doesn’t have a graphical user interface. Able to trade on the following exchanges: Bittrex, Quadria, GDAX, Pollniex and Gemini.
OsEngine
OsEngine is a suite of exchange trading applications. It includes:
- Data – used to load historical data from various sources.
- Optimizer – used to test one strategy.
- Tester – for testing several trading algorithms, but without changing the parameters. It can work simultaneously on several timeframes and instruments.
- Miner – searches for profitable patterns on the chart. The found forms can be used in real trading.
- Trader is a module for trading.
Bollinger lines ) and arbitrage. Can be used on some international exchanges (LMAX, InteractivBrokers and ninja trading available), on
MOEX (Transac,
Quik , Most Asts, Plaza 2, SmartCom) and cryptocurrency exchanges (Bitstamp, Bitfinex, Kraken, LiveCoin, ExMo, Binance, ZB , Bitmex, BitMax). Also compatible with one Oanda Forex exchange. There are other popular Open Source trading advisors, for example, TradingBot, for trading on the Moscow Exchange through the broker Atentis or the simple TradingBot robot.



