The article was created based on a series of posts from the OpexBot Telegram channel , supplemented by the author’s vision and the opinion of the AI. Let’s discuss what profit is in trading and how to calculate it correctly, and what take profit is, how to place an order correctly, when to exit a trade and how to take profit.
What is profit in trading
Profit in trading is the financial profit that a trader receives from successful transactions in financial markets. The main goal of trading is to buy an asset at a low price and sell it at a high price. Therefore, profit in trading can be achieved on the difference between the purchase price and the sale price of an asset, taking into account losses on commissions and interest associated with transactions. Experienced traders develop their strategies based on analysis of data and market trends. They take into account various factors such as economic news, political events, technical analysis indicators, etc. to predict price movements and determine the most favorable time to enter and exit trades.
Profits in trading can be significant, but it also comes with high risks. Bad trades can lead to losses, so risk management is an important part of successful trading.
Trading professionals typically set strict rules to limit losses, use take profits and stop losses, and make decisions based on objective criteria rather than emotions.
Exchange profit is not what you see in the terminal
Let’s sum it up by profit. Profit in trading is the difference between the investments made and the income received. Profit on the stock exchange is your net income, your profit. But profit is always less than income! This is important to remember. From the total income received from the transaction you need to subtract:
- invested;
- broker commissions;
- payment for the terminal and so on.

Important! Profit does not equal income. There may be income, but there may not be profit. If the costs of commissions, terminals and other expenses are greater than the profitability of the transaction, then you are trading at a loss. You drain your deposit, and you can do it unnoticed by yourself.
Read more about why it is important to take commissions into account when assessing the profitability of a transaction, as well as how to do it automatically:
What is take profit in trading
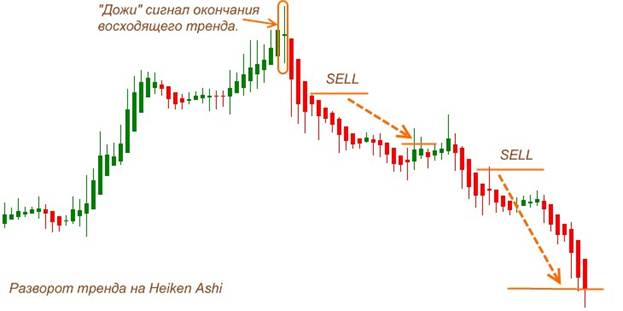
This is a completely different term. Literally “take the profit”. A pending order, which indicates at what price the transaction will be closed and the profit or profit will be recorded. Essentially, take profit is a price level or percentage mark, upon reaching which the trader closes his deal and locks in the profit. This approach is based on the principle of minimizing risk and timely protective action. Take profit is an integral part of the strategy in investing and trading in financial markets. Using an order in combination with a stop loss allows you to control potential losses and manage risk, creating stable preconditions for successful investment activity.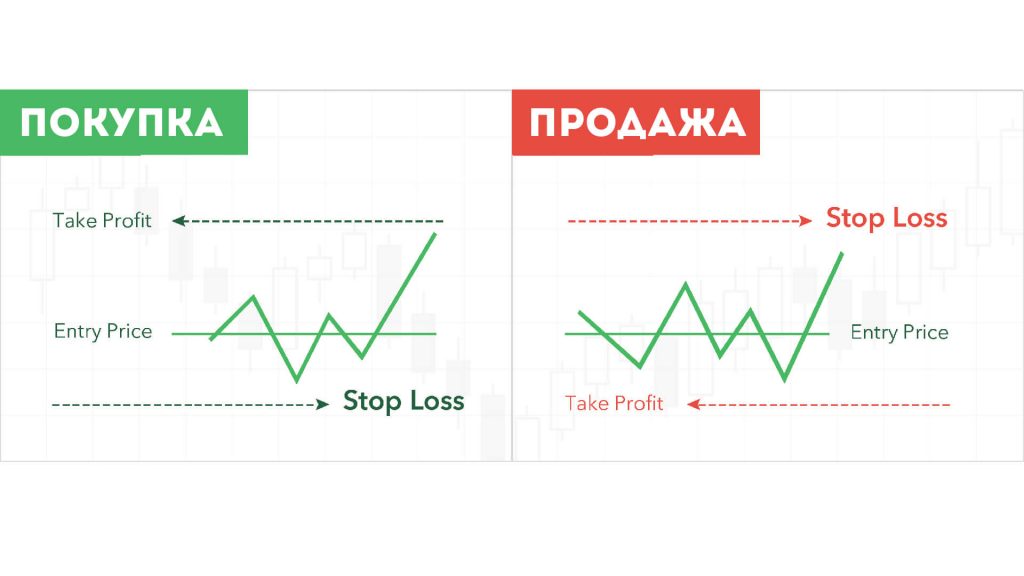
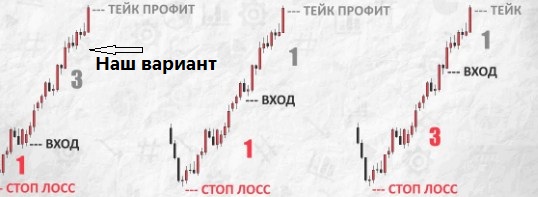
Take profit floating and fixed – which is better?
To skim the cream, you need to exit the trade correctly. And it’s not about the risk/reward ratio. There are two approaches. Floating take profit implies that the trader himself chooses the exit point based on the current state of the market, personal opinion and subjective assessment. The advantage of this approach is that with favorable development, you can get a large risk/reward ratio. For example, 1 to 5. Or, conversely, quickly exit the position at any time. Perfect? Not so simple. You won’t be able to eat fish and ride a scooter.
The main disadvantage of a floating take is excessive emotional stress. It is practically impossible to exit a trade perfectly on the fly.
⁉ Why did you sit out in position? Why didn’t you hold on? Why did you fix it early? Such questions cut like a knife. Dissatisfaction with oneself has ruined more than one hundred generally good traders. In addition, the floating take is one of the dominoes of intuitive trading. Which is emotionally difficult, energy- and time-consuming. Constantly monitoring the deal burns you out and pushes you to take unreasonable actions. Exit points become chaotic. What is a trailing stop ? But it’s fixed